Development of Safe and Effective Batch and Continuous Manufacturing Processes
Continuous manufacturing with cheap raw materials
Development of safe water-based synthesis of 1,2,3 triazole, a versatile reactant in organic synthesis of many drugs and bioactive molecules, using cheap raw materials. This paper moves the synthesis from traditional batch techniques to a continuous synthesis pathway and highlights many of the benefits of doing so.
A Zaiput SEP-200 is used for the aqueous organic phase separation, to facilitate the continuous extraction and isolation of 1,2,3 triazole from the reaction mixture.
Click here to read the full paper
Zaiput phase separator for Continuous Manufacturing
Zaiput’s phase separators are used in the industry for laboratory, pilot and production-scale applications. Researchers in labs around the globe use our membrane based technology to continuously separate bi-phasic mixtures (typically aqueous organic) in industries ranging from Pharma, to Flavor & Fragrances, to Fine Chemicals, and beyond.
The accuracy of the phase separation, the lack of any moving parts, the ability to work without density difference between phases, and the low internal volume, make this device a very common solution for in-line phase separation in flow chemistry labs and continuous manufacturing plants around the world, as shown here.
How it works
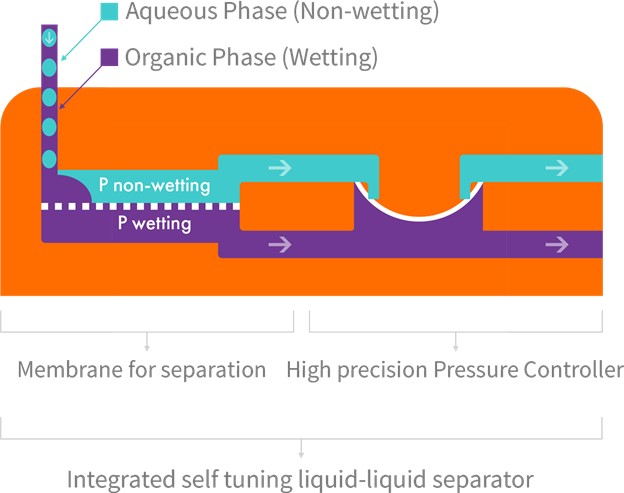
- When a biphasic stream (aqueous phase and an organic phase) enters the separator, one phase will have an affinity for the membrane and fill the pores (this is referred to as the “wetting” phase), and the other phase will be repelled and will not fill the pores (this is referred to as the “non-wetting” phase).
- Once the membrane pores are filled with the wetting phase, a pressure differential is applied across the two sides of the membrane. This pressure differential is finely adjusted by Zaiput’s patented internal pressure controller to apply just enough pressure to “push” the wetting phase without forcing the non-wetting phase through the pores (see figure above). The separator is designed to maintain a constant pressure differential across the designated flow rates for a large scope of chemical systems.
- A key aspect of the technology is that it exploits differences in wettability and surface forces to accomplish the separation; as a result, the device can separate liquids with the same density and emulsions with continuous operation
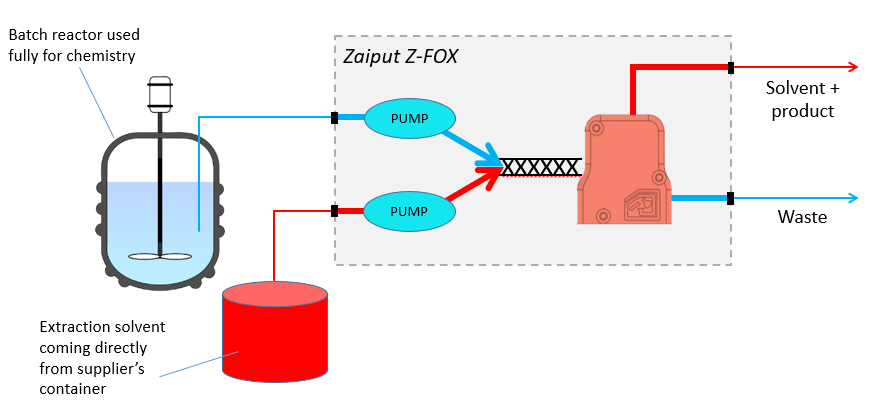
These devices are also used for counter-current extractions, and for enhancing liquid-liquid extractions (LLE) for batch processes, in order to free up space in batch reactors, as shown here: